What is IFSC Code? Full Form, Meaning, and Importance in Banking
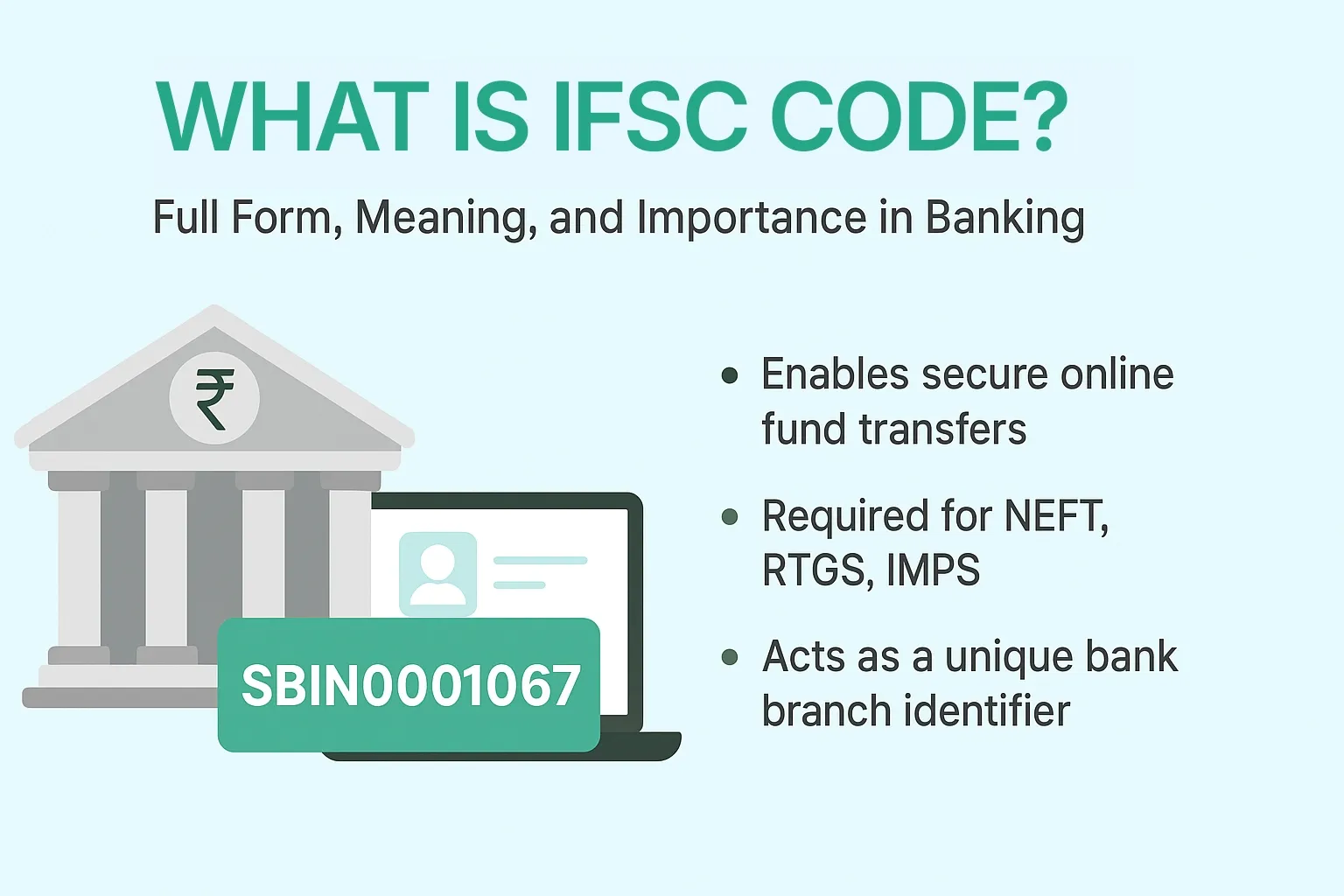
In the age of digital banking, transferring money has become a seamless, everyday task. But behind every successful online transaction is a crucial piece of information that ensures your funds reach the right destination: the IFSC Code.
For many, this 11-character code is just a required field they copy-paste from a bank passbook or website. But understanding what is IFSC code and why it's so important can help you avoid errors and better navigate the world of digital finance.
This comprehensive guide by EximPe will demystify the IFSC Code, explaining its full form, breaking down its structure, and highlighting its vital role in modern Indian banking.
What is the Full Form of IFSC?
The full form of IFSC is Indian Financial System Code.
Issued by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI), the IFSC is a unique code assigned to every single bank branch in the country that participates in electronic fund transfers. It acts as a digital address for that specific branch, ensuring that money sent through online payment systems is routed to the correct destination.
What is IFSC Code in Banking?
In simple terms, an IFSC Code is an 11-character alphanumeric code that uniquely identifies a bank branch in India. The purpose of this unique identifier is to facilitate secure and accurate inter-bank electronic fund transfers within the country.
Without the correct IFSC code, you cannot initiate an online money transfer using popular domestic systems such as:
- NEFT (National Electronic Funds Transfer): A system for transferring funds in half-hourly batches.
- RTGS (Real-Time Gross Settlement): A system for high-value, real-time fund transfers.
- IMPS (Immediate Payment Service): A 24/7 service for instant, inter-bank fund transfers.
The IFSC code serves as a backbone for these systems, ensuring that funds from one bank account are credited to the correct beneficiary's account in another bank branch, even if it's in a different city.
IFSC Code: How Many Digits and What Do They Mean?
An IFSC Code is always 11 characters long and follows a standardized format. The structure is designed to provide specific information about the bank and its branch.
The code is broken down into three distinct parts:
1. The First Four Characters (Alphabetic)
The first four characters always represent the name of the bank. This is a common identifier for all branches of that bank.
- Examples: HDFC for HDFC Bank, SBIN for State Bank of India, ICIC for ICICI Bank, and AXIS for Axis Bank.
2. The Fifth Character (Numeric)
The fifth character is always a zero (0). This character is a control character reserved for future use. Its purpose is to act as a placeholder, separating the bank code from the branch code.
3. The Last Six Characters (Alphanumeric)
The final six characters uniquely identify the specific bank branch. No two branches, even within the same bank, will have the same six-character code. This is what makes the IFSC a precise "digital address" for each branch.
For example, in the IFSC code SBIN0001067, 'SBIN' represents the State Bank of India, the 0 is the reserved character, and 001067 is the unique code for a specific branch.
Why is the IFSC Code So Important?
The IFSC code is more than just a random number; it's a pillar of India's digital financial infrastructure. Its importance can be summarized in a few key points:
1. Ensures Accuracy and Prevents Errors
The unique nature of the IFSC code for each branch eliminates the risk of human error during an online fund transfer. By combining the IFSC code with the beneficiary's bank account number, the system can cross-verify the details and ensure the funds are routed to the exact, intended recipient. Without it, the chances of money being sent to the wrong account would be significantly higher.
2. Facilitates Paperless Transactions
The IFSC code enables seamless, paperless transactions through NEFT, RTGS, and IMPS. This has not only made banking more convenient but has also accelerated the shift towards a cashless economy, streamlining financial operations for both individuals and businesses.
3. Speed and Efficiency
The IFSC code allows for the automation of fund transfers. Once you enter the beneficiary's details, the system instantly validates the information and routes the payment. This automation ensures that funds are transferred quickly, often within minutes or hours, compared to the days it would take for a physical bank transfer.
4. It's Mandatory for All Online Transfers
For any digital inter-bank transfer in India, providing the IFSC code is a mandatory requirement. This uniform standard ensures that all electronic fund transfers are conducted securely and in a traceable manner, which also helps the RBI monitor and regulate the flow of funds within the country.
Is IFSC Code the Same for All Customers of the Same Branch?
Yes, the IFSC code is the same for all customers of the same bank branch. The code identifies the branch, not the individual customer or their account. Every person who holds an account at the same branch will have the same IFSC code associated with their account.
The IFSC code acts like a unique postal code for a specific bank branch. Just as everyone living in the same area has the same postal code, everyone with a bank account at a particular branch shares the same IFSC code.
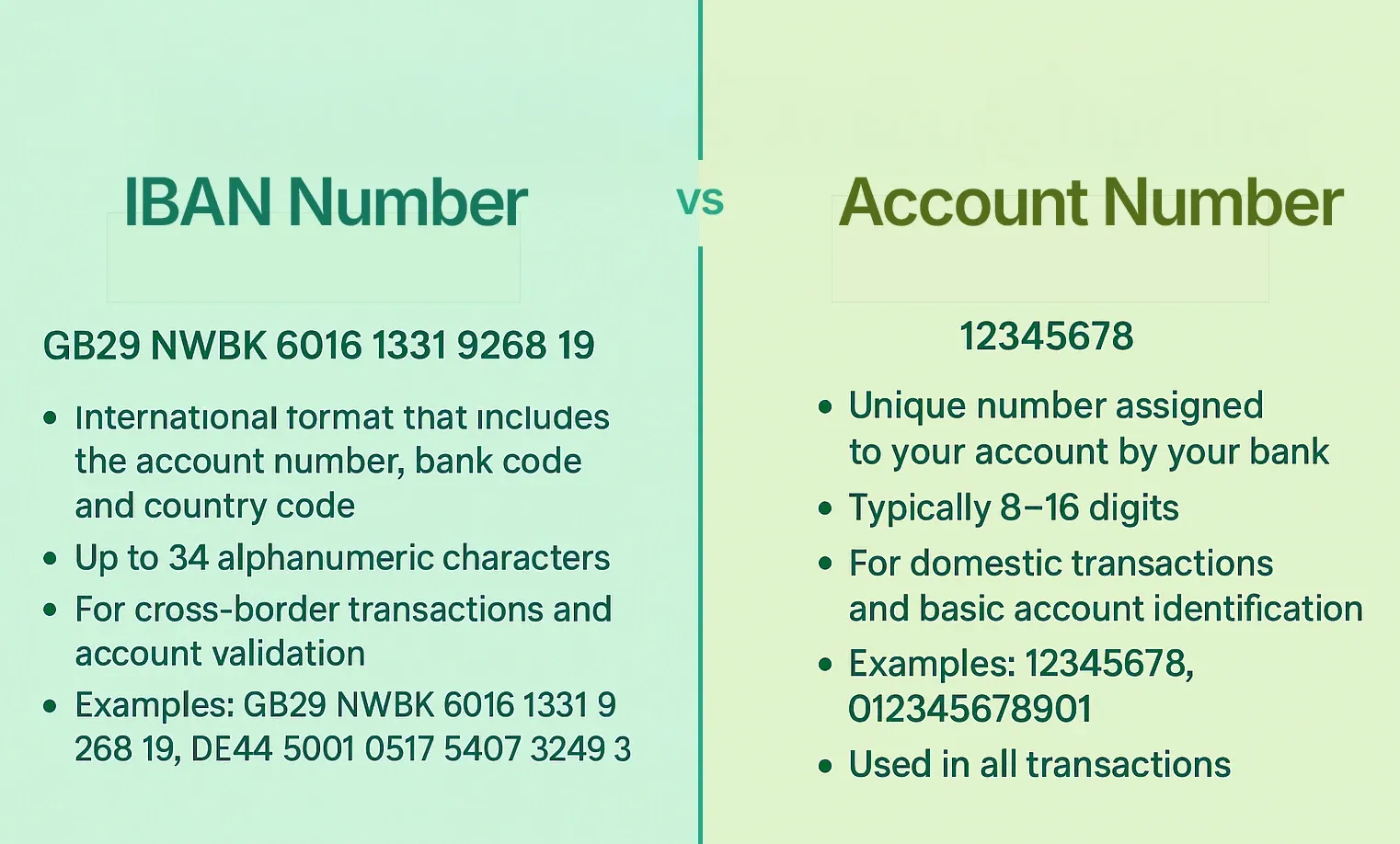
IFSC vs. Other Bank Codes: A Quick Comparison
It's common to confuse the IFSC code with other bank identifiers. Here’s a quick overview of how it differs from a SWIFT code and a local account number:
- IFSC Code: Used for domestic electronic fund transfers (NEFT, RTGS, IMPS) within India. It's an 11-character code unique to each bank branch.
- SWIFT/BIC Code: Used for international money transfers. It's an 8 or 11-character code that identifies a bank globally. For overseas transfers, you will need the SWIFT code, not the IFSC.
- Account Number: Your personal, unique identifier for your specific account at a bank. It is not tied to a specific branch in the same way an IFSC code is.
Knowing the difference is key to a smooth transaction. You use your IFSC code for payments within India, but for a transfer from a client in the USA, you would need to provide your bank's SWIFT code and your account number.
Conclusion
The Indian Financial System Code (IFSC) is a seemingly small but incredibly powerful tool. Its unique, standardized format has revolutionized domestic banking, making electronic fund transfers fast, secure, and highly reliable. By understanding its meaning, structure, and importance, you gain a deeper appreciation for the digital infrastructure that powers India’s economy and ensure your own financial transactions are always on track.
FAQs on IFSC Code
1. What is IFSC code in banking?
IFSC stands for Indian Financial System Code. It’s an 11-character code used to identify a bank branch for online fund transfers.
2. What is the full form of IFSC?
The full form of IFSC is Indian Financial System Code.
3. IFSC code how many digits?
It has 11 characters: 4 for bank, 1 reserved, and 6 for branch code.
4. Is IFSC code the same for all customers of the same branch?
Yes. All account holders of the same branch share one IFSC code.
5. Can IFSC codes change?
Yes, IFSC codes may change after bank mergers or branch relocations. Always confirm with your bank before making transfers.
6. Who provides IFSC codes?
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) assigns IFSC codes to all branches that support electronic transfers.
7. Is the IFSC code required for UPI transactions?
No. UPI uses mobile numbers and virtual payment addresses (VPAs), not IFSC codes.
8. Can I do an international transfer with IFSC?
No. For international transactions, you need a SWIFT code, not an IFSC code.